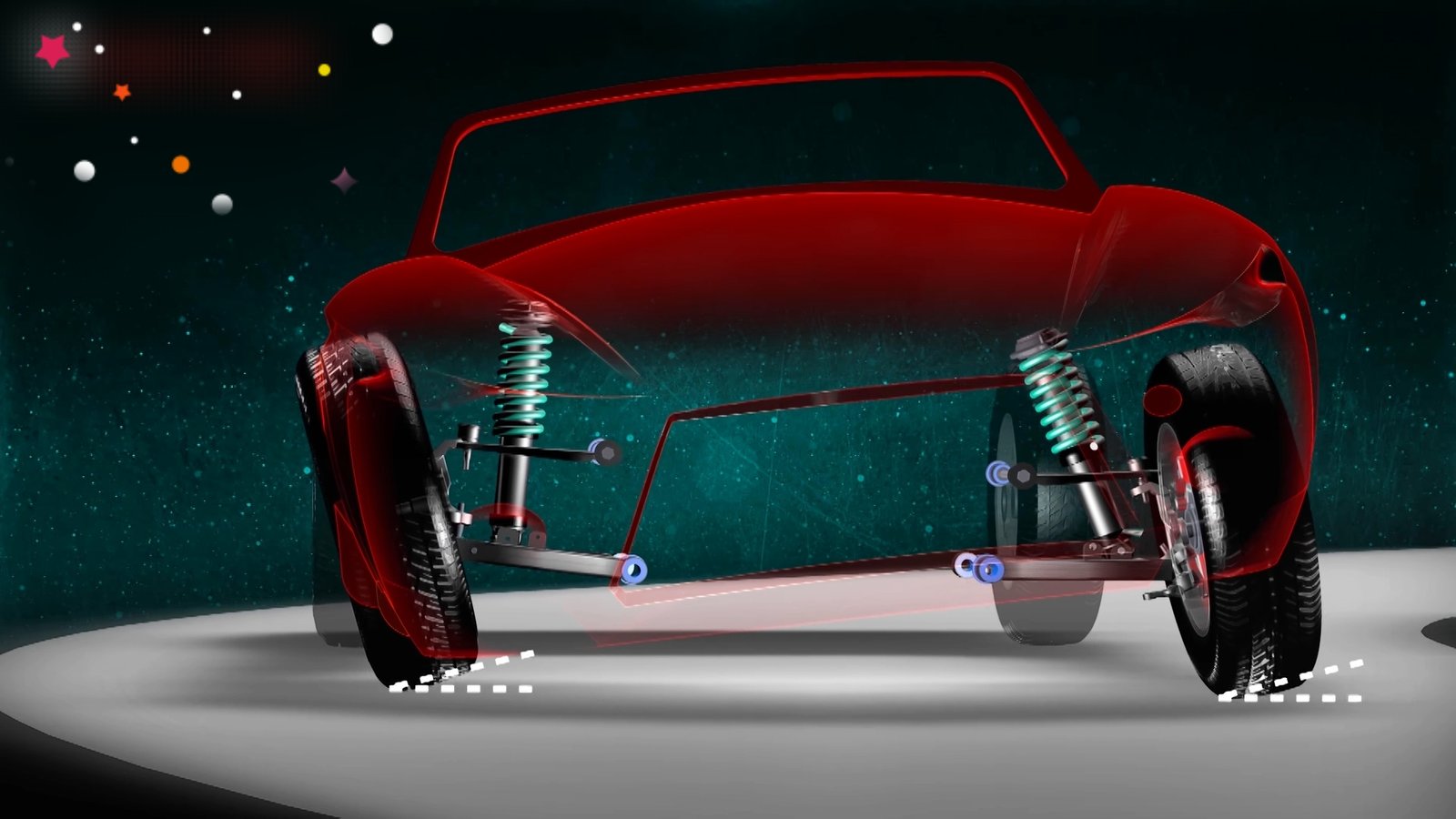
A stabilizer is a part of a car attached to the suspension to prevent the vehicle from tilting and stabilizing driving. It’s also called an anti-roll bar.
If you are concerned about bulge or excessive bending when making a curve, it may be improved by changing the stabilizer settings.
Please note: that these parts are directly related to driving, so if they are set incorrectly or damaged, it may cause a severe accident.
This page explains the role and effects of stabilizers, replacement methods, replacement costs, and setting examples.
Table of Contents
(anti-roll bar) What is a stabilizer?
The word stabilizer comes from the English word “stabilizer,” which means “person who stabilizes,” “stabilizer (of an aircraft),” or “ballast (of a ship).” A car stabilizer is a device that stabilizes driving.
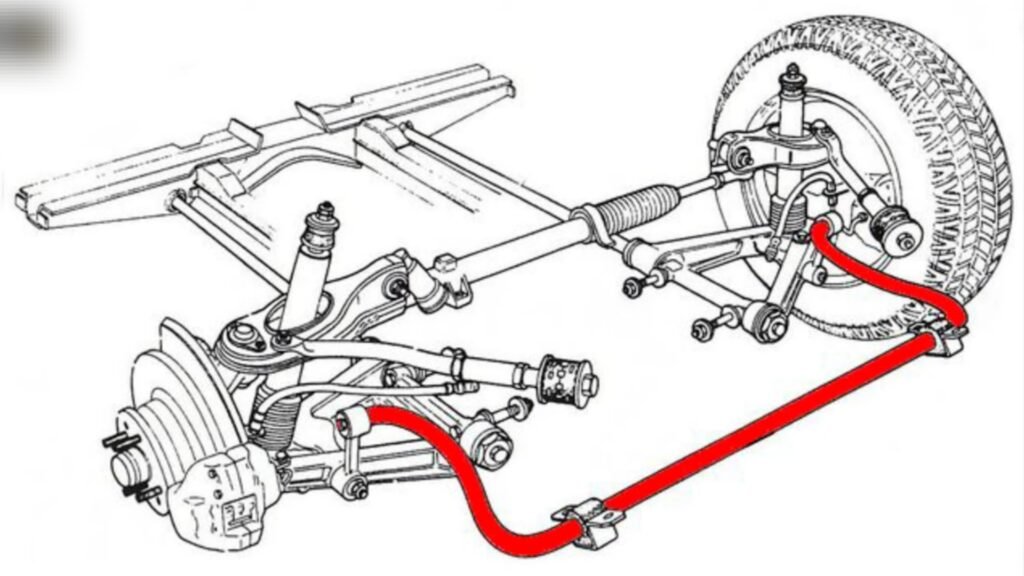
Specifically, it is a U-shaped or U-shaped spring bar-shaped part that connects a car’s left and right suspensions and is installed in many vehicles. This improves ride comfort by suppressing the roll (the force that causes the vehicle to lean from side to side) when turning corners or changing lanes, preventing lateral sway.
The suspension is a device that connects the tires to the vehicle body and cushions vibrations from the ground.
Role and effect of stabilizer
The role of the stabilizer is to reduce roll in corners and maintain a comfortable ride.
In cars without stabilizers, the left and right suspensions move regularly when driving straight. However, the outer suspension contracts when making a curve, and the inner suspension stretches, causing the vehicle to lean significantly outward.
The tilt of the vehicle body caused by curves can be suppressed to some extent by strengthening the suspension. However, if the road is uneven during everyday driving, the car will experience a lot of vertical sway, making the ride uncomfortable.
Some cars don’t have stabilizers.
The stabilizer is not an essential part of the car to run; even if it is removed, the vehicle will not be able to drive.
Some cars do not have stabilizers on either the front or rear wheels or only have stabilizers on either one. In sports cars, etc., there are cases where stabilizers are not installed, and alternative parts are installed.
Furthermore, on rough roads such as uneven mountain roads, the stabilizer bars suppress the suspension’s movement to keep the vehicle level, making the ride uncomfortable.
Some people, such as those who often drive on rough roads, may choose a car model without a stabilizer or remove the stabilizer and change the settings.
What is a stabilizer link?
In addition to stabilizers, you should also know about stabilizer links.
The stabilizer link is a part that secures and supports the stabilizer to the vehicle body. It is a rod-shaped part that connects the stabilizer and suspension and has a mechanism similar to a human joint called a “ball joint.” This mechanism flexibly responds to movements around corners and steps.
The inside of the ball joint is coated with lubricating oil (grease) to prevent the metal from rubbing against each other and is fixed with rubber parts (stabilizer bushings).
About stabilizer settings
The role of the stabilizer is not only to stabilize and support the vehicle body. By adjusting the strength (hardness) of the front and rear stabilizers, you can change the behavior in corners.
What is the strength (hardness) of the stabilizer?
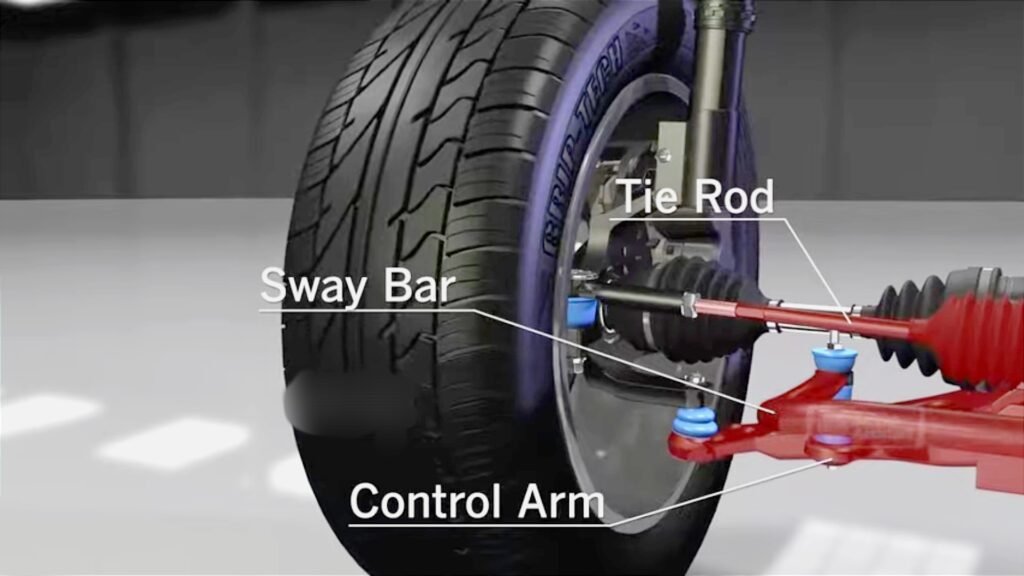
The hardness with which the stabilizer is twisted is called “strength,” and installing a complex stabilizer is called “strengthening.” The more complicated the stabilizer is, the less it will turn, and the more influential the stabilizer will be.
The stronger the stabilizer, the more it will suppress roll in corners. However, if it is too strong, the ride quality may deteriorate, so care must be taken to balance roll control and ride comfort.
Suppose you want to improve riding comfort. In that case, it will be easier to get the desired effect by reviewing the settings, including replacing the stabilizer and parts such as the suspension (spring) and steering shock absorber (damper).
Setting example
We will introduce examples of stabilizer settings for each desired effect. Please note that technical terminology will be used in explaining setting examples, so please refer to the following when reading.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Understeer | When a car bulges outward (doesn’t turn) when entering a corner |
| Neutral Steer | Cornering without bias, such as bulges or cuts |
| Oversteer | Car cutting inward when entering a corner |
| Push Under | When the car is pushed out of the corner by the driving force and cannot complete the turn |
| Steering Wheel | A steering device is used to change the direction of travel |
About stabilizer replacement and costs
We will explain the approximate timing and cost of replacing the stabilizer.
Guidelines and signs for stabilizer replacement
There is no fixed replacement period for stabilizers. However, if you have the following problems, consider replacing it.
| Concern | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| Roll when turning a curve | Settings may need adjustment<br>- Stabilizer may need replacement |
| Shaking while driving | Suspension issues |
| Feeling dizzy when changing lanes | Suspension issues |
| Replacing suspension or changing settings | Suspension settings may need adjustment |
| Upgrading suspension for strength | Stabilizer should also be upgraded for robustness |
| Damaged or deteriorated stabilizer | Inspection and replacement required for safety reasons |
Stabilizer replacement cost
The average price for each stabilizer is approximately 15,000 yen. The labor cost for replacement is about 5,000 yen to 10,000 yen per piece. Including labor costs over 20,000 yen per tire, so replacing both the front and rear, for example, will cost over 40,000 yen.
Furthermore, if you want to replace the stabilizer link, it will cost an additional 10,000 yen. If you also need to replace the stabilizer bush, it will cost anywhere from a few hundred yen to several thousand yen.
Estimated cost for replacing stabilizer
| Exchange details | Estimated main unit cost | Estimated labor cost |
|---|---|---|
| stabilizer | Approximately 15,000 yen (1 bottle) | About 5,000 yen to 10,000 yen |
| stabilizer link | About 10,000 yen (set of 2) | About 3,000 yen to 5,000 yen |
The above prices are based on the supervisor’s knowledge. Prices vary depending on the vehicle and repair business, so please use the listed price and labor charges as a guide.
Can I replace the stabilizer myself (DIY)?
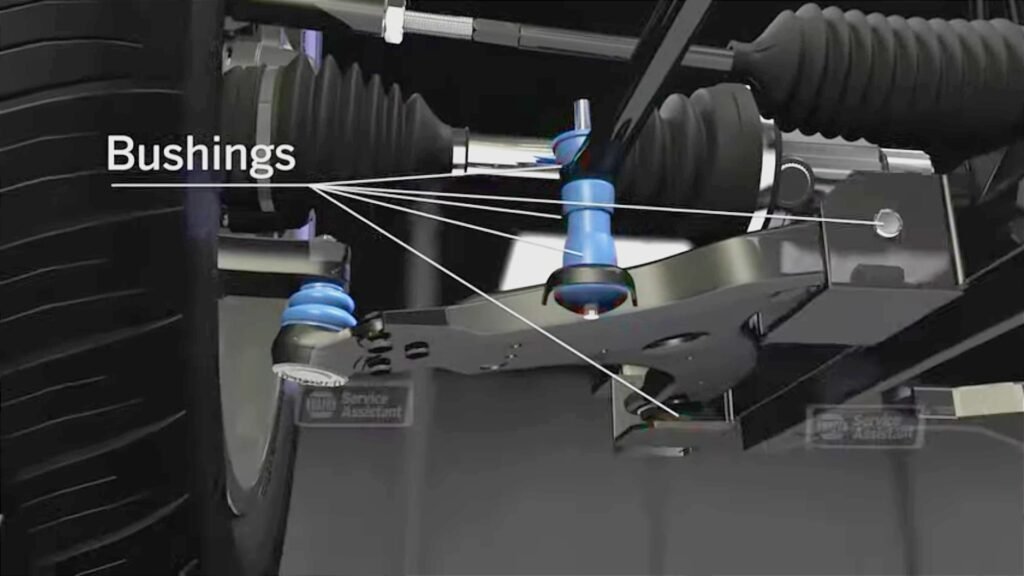
You can replace the stabilizer if you have the parts and tools and follow the instructions. However, it isn’t easy to replace for those not used to it, and assembling the equipment from scratch is expensive. If you are unfamiliar with the procedure, feel anxious, or have difficulty after reading the steps below, please contact your dealer or repair shop for replacement.
Steps to replace
To replace the stabilizer, follow the steps below.
1. Jack up
2. remove both tires
3. Remove the stabilizer bush and stabilizer link
4. Removing and installing the stabilizer
5. Install the stabilizer link and stabilizer bush
6. Install the tire and lower the jack
1. Jack up
A pantograph jack puts tension on the suspension, so you cannot remove the stabilizer link. Use a garage jack to raise both wheels horizontally. After jacking up, install a “rigid rack” (commonly known as a horse) at the bottom of the vehicle for safety.
2. Remove both tires
Remove both tires. The removed tires should be hidden under the vehicle’s body to prevent them from getting caught on the ground if the rigid rack comes off and the car falls.
3. Remove the stabilizer bush and stabilizer link
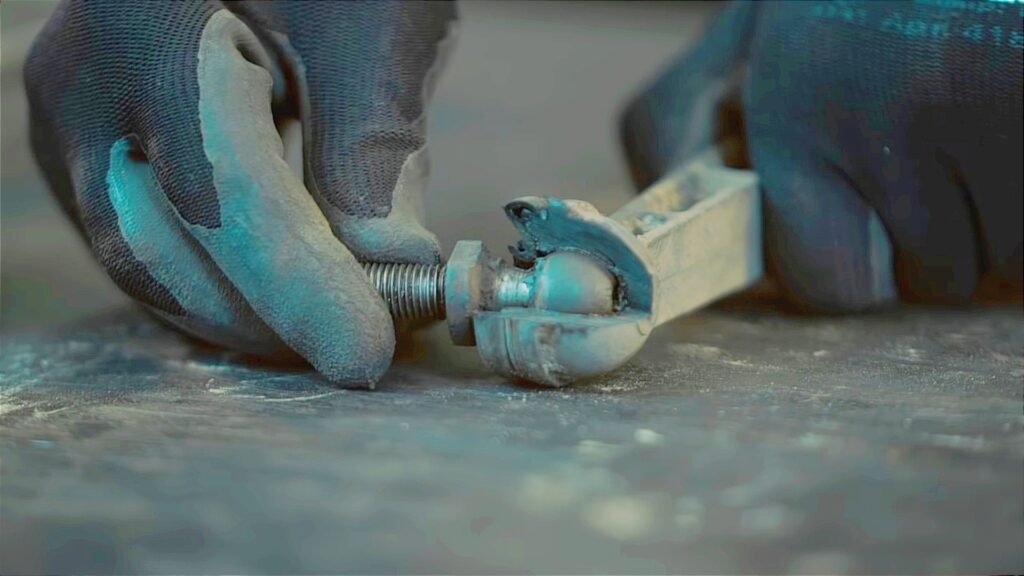

The stabilizer link is fixed with two nuts, so remove it by turning it with a wrench. If a locking nut is attached, insert a hex wrench into the bolt tip and remove the nut.
Once the stabilizer link is removed, remove the bushing that secures the stabilizer to the vehicle body. The stabilizer bushing is also only fixed with bolts, so it’s not difficult to remove.
4. Attaching and detaching the stabilizer
Remove the original stabilizer and install the new stabilizer.
5. Install the stabilizer link and stabilizer bush
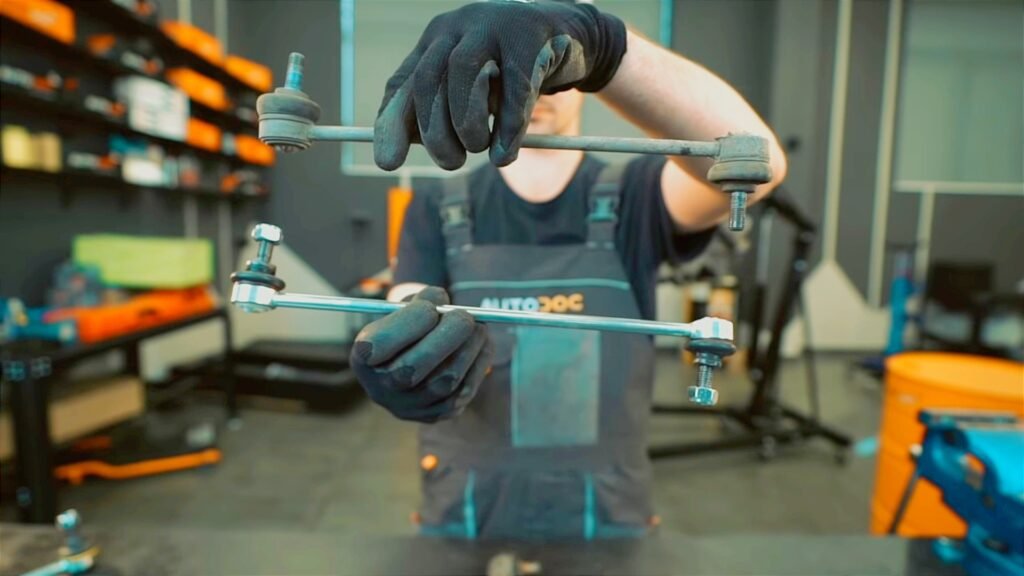

Install the stabilizer link and stabilizer bushing in the reverse order of removing them. When replacing the stabilizer, it is recommended that you also return the stabilizer link and stabilizer bush with new ones.
6. Install the tire and lower the jack
You’re done once the tires are installed and the jack is lowered. It can take 30 minutes to an hour to complete each session, even for those who are used to it, and several hours for those who are not.
Although the way it is installed differs slightly depending on the car model, the method of replacing the stabilizer is almost the same. Before starting work, please take a picture of the undercarriage with a smartphone or similar device to see how it is installed and check that it is correctly put back together after replacement.
Points and precautions when replacing it yourself
If you decide to replace the sway bar yourself, check whether it will fit your car before purchasing.
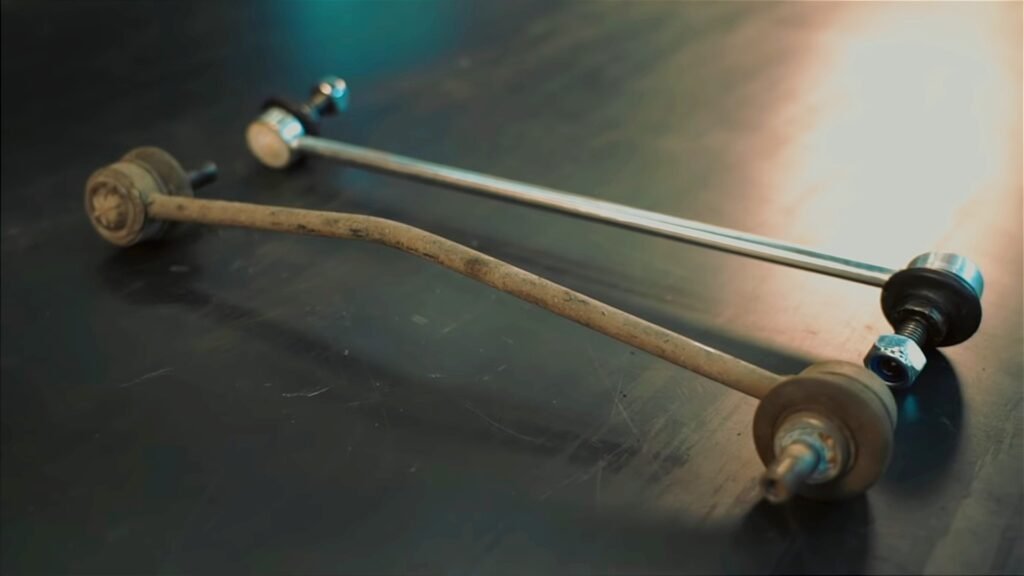

Also, since the stabilizer is a part of the suspension, the nuts that secure the stabilizer or stabilizer link may need to be fixed and difficult to remove. If you try to remove it by force, there is a risk of damage, so if it does not come off, apply lubricant or scrub it with a brush before removing it.
The following parts and tools are required to replace the stabilizer.
· Stabilizer body
· stabilizer link
· stabilizer bushing
· nut
· Hex wrench
· garage jack
· box wrench
· Ratchet wrench
The nuts’ size may differ depending on the manufacturer and car model, so be sure to check beforehand.
Conclusion
The stabilizer is a part that suppresses roll when turning corners. Cornering and ride comfort change depending on the settings, so this is a profound part for those who want to adjust it to their preference.
We recommend replacing the stabilizer if you are concerned about stability, such as rolling around corners. If you find any damage or deterioration, please return it immediately.
Unless otherwise specified, the content of this article is an explanation of the effects and roles of general stabilizers, as well as replacement methods and costs. Please check with the manufacturer or maintenance shop for information on replacing the stabilizer, including the price.
FAQ’s
What happens if the stabilizer link breaks?
The stabilizer link plays the role of suppressing lateral body tilt and improving handling and stability. If the link boot breaks, the grease inside the stabilizer link may leak out, causing abnormal noises and shaking of the vehicle.
How much does it cost to replace a stabilizer link rod?
So how much will it cost to replace it? The parts costs vary depending on the car model but are generally around 2,200 to 5,500 yen. In our case, it costs 5,500 yen to 11,000 yen per location, including labor. Replace the stabilizer link rod before the rubber boot part breaks.
What is the reason for replacing the stabilizer link?
If you are concerned about the car’s instability due to large body roll when turning a curve, replace the stabilizer. If your vehicle becomes unstable and tends to wander when changing lanes on the highway, we recommend replacing the stabilizer. You can change lanes smoothly and drive stably.
When is it time to replace the stabilizer links?
Unlike consumable parts such as tires and batteries, stabilizers do not have a fixed replacement period. The links and rubber bushings used in the mounting parts are prone to deterioration.
What are the symptoms of stabilizer link deterioration?
If there is a problem with the stabilizer link, strange noises such as rattling or clicking may occur from the undercarriage, and grease may leak or smear on the boots of the stabilizer link. Abnormal noises will arise if there is a problem with both types, but grease leakage and smearing are symptoms that only appear with ball joint types.
Do I need a stabilizer?
Effects of Stabilizers When a car turns a curve, it rolls to the left or right, causing it to lose stability. Not only on curves but also when there is a crosswind, there is a risk that the wind pressure will cause the car to tilt and lose stability. To improve the vehicle’s strength, the roll problem must be resolved.










